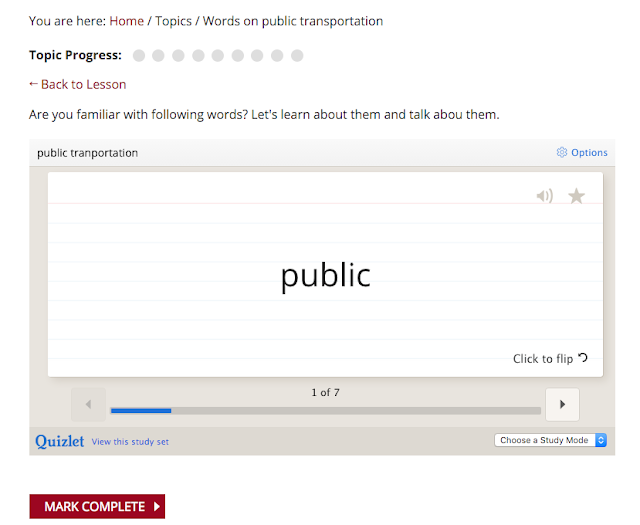
Table 4.
Gagné’s (1984) nine events of instruction and examples in the OLE
Gagné’s (1984) nine events of instruction
|
Examples in the OLE
|
Attention from the students
|
Images, videos, and cartoons can be used to get attentions from students
|
Notification of the objectives
|
Students could be informed of the objectives through a clear written form or a spoken language.
|
Recall of previous learning
|
Students previous learning in native culture and native language is recalled to learn target culture and target language.
|
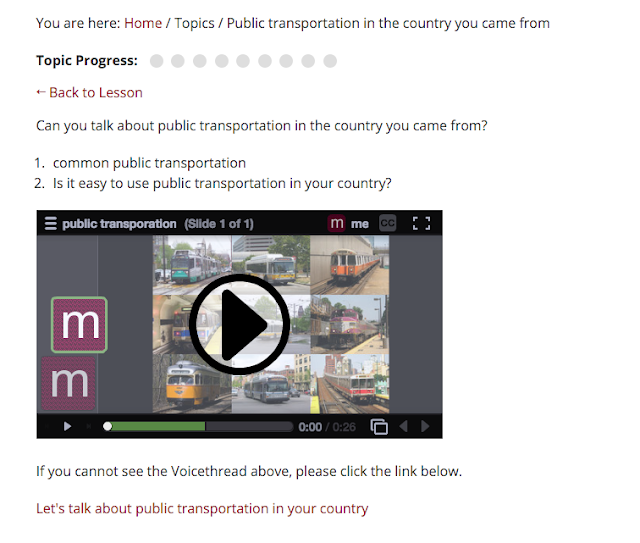
Content presentation
|
Cultural content is provided through online courses. The content is delivered by tools or media such as Quizlet, Youtube, and images.
|
Learning guidance
|
Guidance to learning and tasks is provided through question and answer forum. In addition, the OLE has course progress bar that tells the learners what to take further.
|
Students’ performance
|
Students are supposed to speak and write in target language in the OLE.
|
Feedback
|
Students are getting feedback about their activities through Voicethread and Google Drive
|
Assessment
|
Students’ words activities, speaking activities, and writing activities are assessed to measure their learning outcomes.
|
Enhance and transfer
|
Review section and reflection section are given at the end of online courses.
|